Rainfall consists
of water drops of size 0.5 to 6 millimeters. It is the major form of
precipitation, so first, we need to have an understanding related to the
measurement of rainfall. It is expressed in terms of the depth of rainfall to
which it would cover a horizontal projection of the earth’s surface. We are
assuming that there is no loss by evaporation, runoff, or infiltration. So here
the assumption that we are making is that whatever rainfall depth is coming is
not having any loss, there is no loss from this rainfall. Rainfall is expressed
in terms of millimeters or centimeters. If we are getting rainfall of
2.5milimeters or above, we will be considering it as a rainy day.
Rain gauge
A rain gauge is an instrument used to collect and measure precipitation.
Different types of gauges are non-recording rain gauges and recording rain gauges.
As the name suggests one is the recording type, which will automatically record
how much is the rainfall depth, the other one is non-recording it will not be
recording we can manually measure how much is the rainfall. Nowadays, most
non-recording gauges have been replaced by recording types of rain gauges.
Non-Recording rain gauge (Simon’s rain gauge)
It consists of a cylindrical container that is installed inside the concrete
block as shown in fig.1. A collecting bottle is installed within this
container. The capacity of this bottle is known to us, and a funnel is provided
at the top with its shank inserted in the neck of the receiving bottle. When we
are experiencing rainfall, it will be collected in the bottle. During rainy
days it will be exceeding beyond the capacity of this collecting bottle. So, on
such days during heavy rain and rainy days, we need to take the reading 3 to 4 times
a day because the amount of rainfall will be exceeding the capacity of the rain
gauge., in that case, we need to replace the bottle.
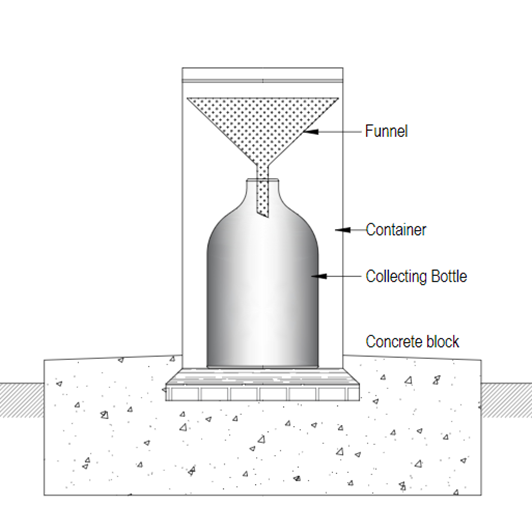
Fig 1. Tipping bucket type rain gauge
Recording
Type Rain Gauge
·
Weighing
bucket type
·
Tipping
bucket type
·
Floating
or natural syphon type rain gauge
Weighing bucket type
Weighing bucket-type
rain gauge consist of a receiver bucket supported by a spring or some other
weighing mechanism, so the working principle is based on the spring action. When
the weight on this bucket is increased, spring will be compressed, and spring
action will determine how much rainfall is occurring. From fig 2 the collecting
bucket is initially empty, and we are having funnel at the top, at the mouth of
the outer cover there is a mechanism. So, the mechanism is connected to the
spring unit, which is a balanced linkage mechanism that is connected to the
spring and the bucket as there is a revolving drum with a chart attached. On
this chart, the rainfall reading is marked. Along with the balance linkage
mechanism, a pen is attached that is marked with red color this is the pen arm.
When rainfall is occurring that is the movement of the bucket due to its increased
weight is transmitted to the pen and recorded on the chart. When the pen is
recording the details, it gives us the plot of accumulated rainfall values
against the elapsed time.
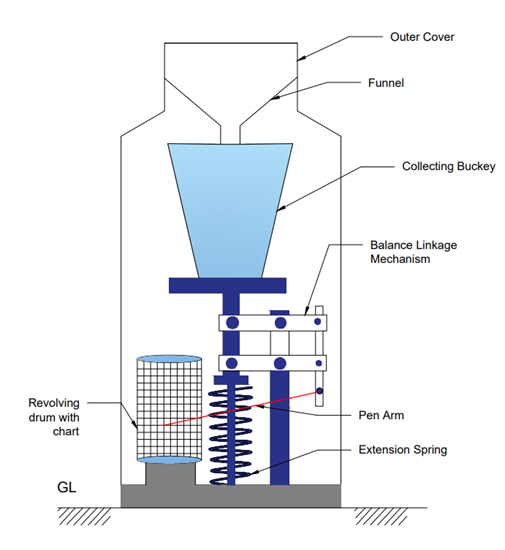
Fig 2. Weighing bucket-type rain gauge
Tipping Bucket Type rain gauge
Tipping bucket rain gauges has got a sharp-edged receiver and at the end of the receiver is provided with a funnel below that a collecting system is there. A pair of buckets are connected under this funnel in such a manner that when one bucket receives 0.25mm of rainfall the bucket will be tipping that is it will be moving in a direction and another bucket will be located beneath the funnel. So whatever rainfall is collected in the bucket will be discharged to the container. After that, the second bucket will be filled, and it will be moving in the other direction. The first bucket will be taking the initial position beneath the funnel and this process will be continuously happening, there is a seesaw mechanism that is taking place there. Fig 3 is the closing view of the tipping buckets and a magnet that is connected to them. This tipping bucket recording is taking place based on this magnetic action. The stationary magnet will be transmitting the signal to a transmitter or to a data logger. The time between two successive tipping indicates the time taken for the occurrence of 0.25 mm precipitation.
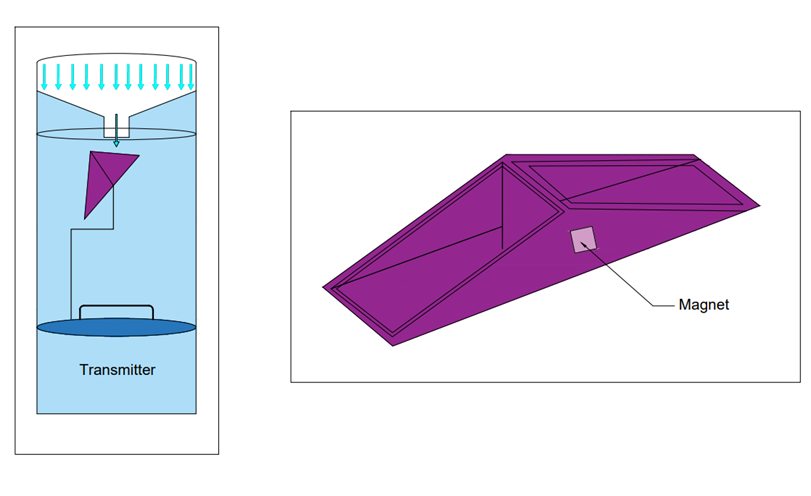
Fig 3. Tipping Bucket type rain gauge
Floating or natural syphon type rain gauge
The working
of a floating-type pressure gauge is similar to weighing a bucket rain gauge. From
fig.4, The funnel will be collecting the rainfall and it will be transferred to
a float chamber and a float is provided at the bottom of the container. Besides
the float chamber, we are having a siphon chamber installed near the float. The
funnel receives the water, when the water level is in the float chamber then
the float will rise, and its movement is recorded by a pen moving on a recording
drum. When the float rises, this float reaches to top and the syphon comes into
operation and releases the water outwards through the connecting pipe, thus all
water in the box is drained out. The movement of this float, the movement is
marked on the chart by means of a pen.
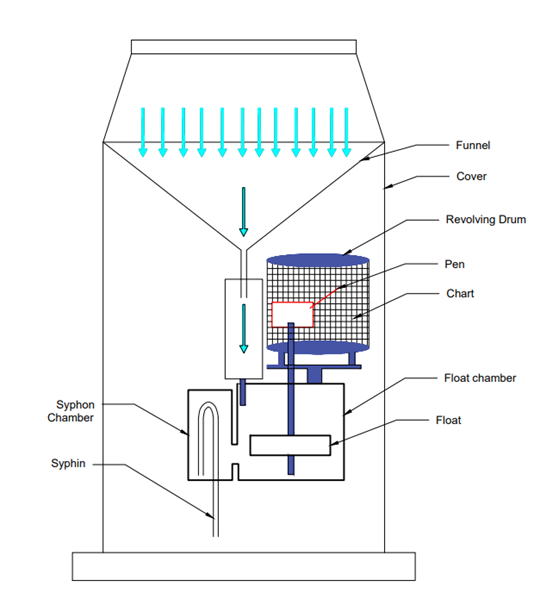
Fig 4. Floating or Natural syphon type rain
gauge
.png)
No comments yet. Start a new discussion.