Lack of Water significantly reduces plant growth. Moisture stress does have an impact on the development of plant organs, which can have a major impact on plant growth. Water stress can affect the initiation and differentiation of vegetative and reproductive organs, as well as cell division and organogenesis. Grain crop yield is partly influenced by the size of the vegetative organs, hence yield is generally determined before heading or blooming. There are various factors that influence the size of plant vegetative organs, and they are intricately linked. Environmental elements play a large part in determining vegetative development, and nitrogen, soil temperature, and soil water are among the most important. In this study, we describe a sensor-cloud-based precision agricultural system for effective water management in agriculture.
1. What kind of sensors are used in smart agriculture?
1. What kind of sensors are used in smart agriculture?
1.1 Optical Sensors in Agriculture
Optical sensors detect multiple frequencies of light reflectance in the near-infrared, mid-infrared, and polarised light spectrums to determine soil qualities. Vehicles, drones, aerial platforms, and satellites all have sensors. Data on soil reflectance and plant color is collected and analyzed. Clay, organic matter, and moisture content of the soil can all be determined using optical sensors.
1.2 Electrochemical Sensors for Soil Nutrient Detection
1.2 Electrochemical Sensors for Soil Nutrient Detection
Soil monitoring is rising as a key component to manipulate clever farming which has been encouraged to have low-cost meal protection and security. Among numerous improvements as an instance net of factors assisted farming, electrochemical sensing machine are becoming reputation through detecting one or more than one soil element effectively, efficiently, and selectively for soil best evaluation remotely through records sharing and location of the region much like point-of-care soil health care. Considering scenarios, this angle is designed to explain the state-of-the-artwork electrochemical sensing era advanced for soil best. The related challenges, viable alternatives, and ability possibilities also are mentioned in this perspective.
The benefits of potentiometric electrochemical sensors are stimulating interest in their programs in soil nutrient detection. They have the potential for computerized multi-goal speedy detection of soil nutrients. As such, they may be additionally confronted with the task of their reliability. Advanced engineering technology has opened our thoughts and furnished new strategies for soil trying out to comply with the KISS (Keep It Simple and Stupid) precept to deal with the complicated soil by trying out techniques with easier techniques at a decreased cost.
1.3 Mechanical Soil Sensors for Agriculture
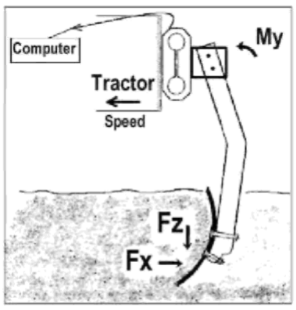
The sensor become stimulated from the principle used when instrumenting soil tillage tools to decide the desired traction. It was made of a cutting blade shifting horizontally in the soil (Fig. 1). This blade was submitted to solicitations, and decreased to draft force (Fx) and vertical force (Fz). The sensitive part of the sensor becomes an octagonal ring transducer fixed out of the soil between the tractor and the beam supporting the blade. It measured Fx, Fz, and the instant My. The detection gadget becomes made from stress gauges, successfully positioned, and related to representing 3 Wheatstone bridges measuring Fx, Fz, and My without interference.
What is Precision Agriculture?
Farmers can mitigate their environmental effect through conducting climate-friendly farming practices like organic farming, which makes use of much less electricity and produces much fewer pollutants than traditional farming, and carbon sequestration, wherein they plant vegetation that clearly cast off carbon dioxide from the air and keep it withinside the soil. Or, they can use technology that permits precision agriculture. Precision agriculture leans on technology to screen and optimize the whole lot from device and fertilizer to water and soil. Often cloud computing is used to collect, examine and keep agriculture statistics. Cloud-linked wi-fi sensors capture statistics from the sphere and device learning algorithms examine that real-time information, giving farmers a higher knowledge of vegetation situations. Sensors can usually screen soil situations like moisture, pH, protein content, nutrients, and temperature.
The use of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) in precision agriculture will increase the efficiency, productivity, and profitability of many agricultural manufacturing systems. Real-time environmental data may be remotely accrued from the rural fields and transferred to wherein it is able to be processed to find out problems, save data, and/or take wanted actions. This contrasts with the traditional agricultural approaches in which decisions are taken based on a few hypothetical common conditions, which won't replicate reality.
The use of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) in precision agriculture will increase the efficiency, productivity, and profitability of many agricultural manufacturing systems. Real-time environmental data may be remotely accrued from the rural fields and transferred to wherein it is able to be processed to find out problems, save data, and/or take wanted actions. This contrasts with the traditional agricultural approaches in which decisions are taken based on a few hypothetical common conditions, which won't replicate reality.
What is an Intelligent water management system?
Water is one of the world's most considerable substances. However, it's also speedy turning into one of the planet's maximum burdened resources. Access to easy water is a crucial difficulty that influences monetary activity, development, and enterprise across the world. Increasing regulatory pressures, weather change, getting old workforces, failing infrastructures, and developing awareness of social obligation and environmental threat control are forcing groups to re-evaluate the effect of water control on their monetary well-being.
How IoT can help in water management?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of devices, data, and different technological capabilities to run any operation greater intuitively with the minimum manual intrusion. IoT has steadily unfolded throughout normal lifestyles and the economic landscape. The fourth commercial revolution (Industry 4.0) idea is extremely primarily based totally on IoT’s intuitive edition and smart automation in each commercial activity.
In the last few years, IoT has additionally entered water and wastewater control. Many local governments and municipalities have commenced the usage of sensor-primarily based totally technological functions to “smartly” run their operations. Moreover, industries are the usage of IoT clever water control to streamline the features in their effluent treatment plants.
In the last few years, IoT has additionally entered water and wastewater control. Many local governments and municipalities have commenced the usage of sensor-primarily based totally technological functions to “smartly” run their operations. Moreover, industries are the usage of IoT clever water control to streamline the features in their effluent treatment plants.
IoT in water control helps utilities reduce dangers that could exist in sewer networks, and water distribution networks, in addition to each water and wastewater treatment plant. It presents the inspiration of data-pushed application control that also can be implemented for greater powerful asset control and operational efficiency.
Since IoT has ended up a buzzword withinside the industry, more organizations are beginning to incorporate it into their systems. However, a lot of them attempt to do it in a rush and fail to make the most of IoT’s clever capabilities. The most routine trouble that agencies face in making the best of IoT in water is their incapability to deal with full-size records volumes.
It is essential to apprehend that the telemetric statistics acquired from IoT sensors are simply one piece of the puzzle. If you can't use these statistics correctly, setting up IoT clever water control will now no longer supply actionable results to enhance control of water at each public and private operation.
These are ways you can make sense of IoT data and use it to streamline your water management.
.png)
No comments yet. Start a new discussion.