What is evapotranspiration or ET? What is its relevance in irrigation? Read more to know more.
Evapotranspiration
The combination of two different processes of water loss through evaporation from the soil surface on the one hand and transpiration from crops, on the other hand, is called evapotranspiration (ET). A commonly used experimental method to measure the evaporation rate is by using Lysimeter and also Field plots.
Lysimeter
Lysimeter is a water-tight tank containing soil and it is set in a field, which is having growing plants. Some plants grown in the tank, are present in the surrounding field. So, in order to maintain a similar condition as that of the field condition, we will be growing the same kind of plant in the Lysimeter also.
Evapotranspiration is estimated in terms of the amount of water required to maintain constant moisture conditions within the tank. So, we will be maintaining a particular soil moisture condition within the soil, that used to be measured by using soil moisture sensors. So, for that, we will be continuously watering at regular intervals to maintain the soil moisture to be at a constant level. So based on the water, which is added to the Lysimeter, we can calculate how much water is lost to the atmosphere due to evapotranspiration.
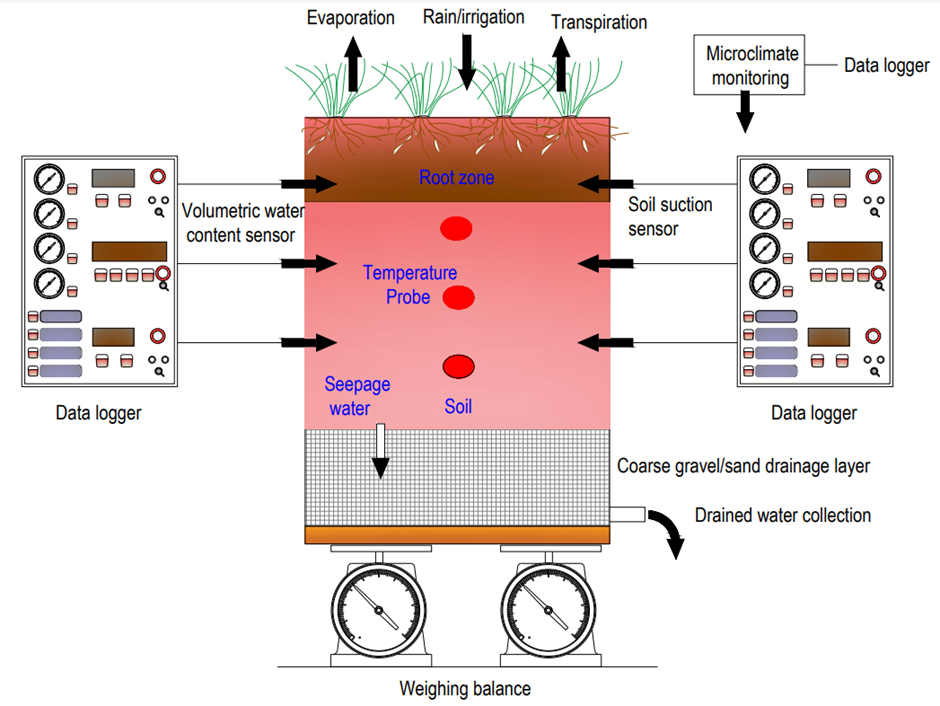
Fig 1: Working of Lysimeter
Let us see an engineered Lysimeter, fig 1, So we are not completely filling the tank with soil, it will be having different layers, bottom layer is fixed for draining the water. So, in this region, we will be filling the coarse gravel or sand. Above that, we will be filling the soil and the upper part is the root zone and will be growing different plants. These plants are chosen in such a way that we will be considering the similar kind of Plants which are grown in the field, where we need to determine evapotranspiration. This is mainly used in the agricultural fields and we will be watering the plants at regular intervals, irrigated water, or sometimes due to rainfall the plants will be getting water. And from the vegetated surface evaporation will take place and from the plant leaves transpiration will be taking place. And regarding the atmospheric parameters, microclimate monitoring will be giving us, if you are monitoring the atmospheric parameter such as temperature, rainfall, vapor pressure, and wind velocity, all these can be obtained from the microclimate monitoring system and that will be connected to the sensors, that will be connected to the data logger and that will be transferring the data to the computer. And now regarding soil pressure, that measurement will be done by means of sensors at different levels these sensors will be installed. So, these will be soil moisture sensors, that also will be connected to a data logger.
Finally, data will be available to us on our computers. Then we will be having the temperature probes within the soil in order to understand the prevailing temperature within the soil. And also soil moisture sensors and volumetric water content sensors will be present and which are also connected to the data logger and finally the data will be transferred to the computer. And the water due to rainwater or irrigated water, soil moisture which is present in the soil, soil moisture will be increasing. Excess moisture will be connected at the bottom as seepage water and that will be collected through this drainage pipe, which is provided at the bottom. The drained water can be measured by means of a weighing balance. So this is the principle of a Lysimeter. So this is the basic methodology behind the working of a Lysimeter. Always these sensors are not available, in that case, the quantity of water that is added to maintain constant water moisture will be measured. So, for that, we will be having the volumetric moisture content measuring sensors installed within the Lysimeter. Now the second way of conducting experiments is by means of field plots.
Field Plots
In field plots we are not taking separately a tank or pan or anything like that, a separate field is considered, and special plots with all water budget elements are known. In that case, we need to know all the parameters, which are required for the water balance equation. And then we will be making use of the water balance equation evapotranspiration given by
ET = P+I-R-ΔS
This is nothing but our water balance.
ET - Evapotranspiration
P – Precipitation
I – Irrigation input/Inflow.
R – Runoff
ΔS – Change in soil storage
So by making of these we can calculate the evapotranspiration by conducting experiments, either by using the field plots.






.png)




No comments yet