Rain Water Harvesting
A blog on rain water harvesting and its importance.
Rainwater harvesting is the process of storing rainwater in such a way that it can be used throughout the year. It is the collection and storage of rainwater instead of allowing it to run off. Rainwater is collected from the roof or a roof-like surface and redirected into a tank, well or reservoir, so that it flows downstream and restores groundwater. Rooftop harvesting is the most common way of rainwater harvesting and is used for domestic and agricultural purposes. Water from flooded rivers can be stored in small ponds. Collected rainwater can be transferred into percolation tanks to facilitate discharge into ground.

Importance of rainwater harvesting
Only 2.5% of the world's water is freshwater, most of which is in the form of polar ice caps. An average person consumes 340 litres of water per day and the average family consumes 900 litres of water per day. About 60 litres of this is for toilet flushing. Surface water is insufficient to meet our needs and we must depend on groundwater.
And this is why rainwater harvesting is important. It provides a good supplement to other water sources thus relieving pressure on other water sources. Rainwater is a clean and pure source of drinking water and requires low chemical treatment as the number of pollutants is very low.
How can we make use of the harvested rainwater?
We can use
the collected water for;
1. Drinking
2. Cooking
3. Agricultural purposes
4. Toilets (Bathing and Flushing Toilets)
5. Gardens irrigation
6. Water for pets, wildlife, livestock
7. Pools and
other water bodies
8. Washing vehicles and equipment
9. Fire Protection-Composting
Components of a rainwater harvesting system
1. Rainwater filter: Rainwater harvesting
filters are important in making any rainwater harvesting system usable and are
used to filter out rainwater runoff from the collection roof before entering
the storage tank.
2. Inflow
3. Floating intake filter
4. Wall bush: To protect cables and PVC pipe from damage.
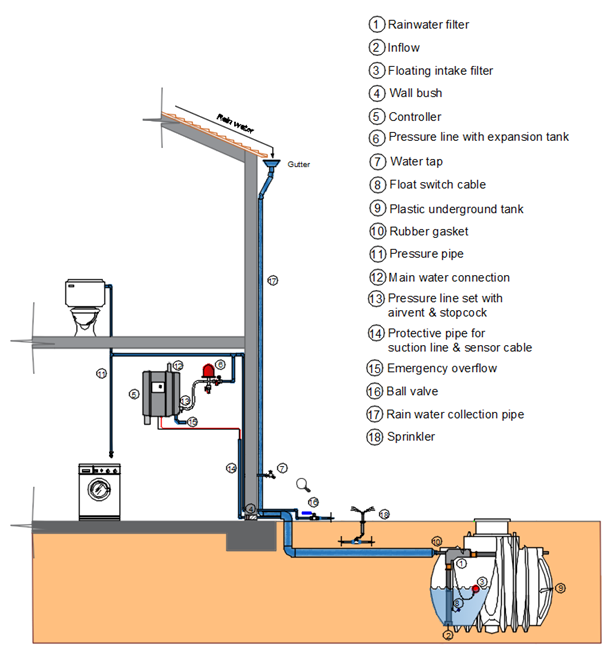
5. Controller: To control RWH system.
6. Pressure line with expansion tank
7. Water tap: For outdoor purpose like car wash
8. Floating switch cable: water lever pumps off
9. Plastic underground tank: Tank
can be accommodated under parking areas or driveways to save space. Underground tanks must be measured for decades of
useful life, soil and traffic congestion. Underground tanks are made of many
materials, the most common of which are PE, PP, GRP and concrete.
10. Rubber gasket
11. Pressure pipe: They are usually 25 mm in diameter
12. Main water connection: Municipal line
13. Pressure line set with air vent & stopcock: Automatic
vent valves are used to remove air inside the heating system. The air
circulating in the pipes can cause several problems to metal parts. A stopcock
looks like a tap, but without an outlet spot. It will be between two lengths of
pipe, acting as a connector. This allows the water flow to be blocked when the
stopcock is closed.
14. Protective pipe for suction line and sensor cable: 25mm PVC
15. Emergency overflow
16. Ball valve: A ball valve is a shut-off valve that controls
the flow of fluid using a rotary ball with a bore. By rotating the ball 90
degrees around its axis, the medium can flow or block.
17. Rainwater collection pipe: To collect rainwater from roof to
storage tank. Rainwater bottom pipes are usually circular but can be any shape.
They are usually 50-150 mm in diameter
18. Sprinkler Irrigation: Sprinkler irrigation is a method of applying
irrigation water like natural rainfall. Water is usually pumped through a
piping system. It is then sprayed into the air by sprinklers so that it
decomposes into small droplets that fall to the ground.
Advantages
- It provides
self-sufficiency to water supply.
- Rainwater harvesting is less
expensive, easy to construct and easy to maintain.
- Slow down water flow, contains
potential floodwater and reduces spread of pollution..
- The water is convenient and
accessible; valuable time and effort are saved in collecting and/or hauling
water.
- It provides a supply of water
to meet our future needs.
- It can save up to 50% of water for reuse.
- Improves sustainability of water use.
- Rise in the water levels in wells and bore wells
that are drying up.
- Mitigation
of the effects of drought.
- Soil
erosion decreases as surface water flow decreases.
- Reducing
the suffocation of rainwater canals and flooding on roads.
- The construction, operation and maintenance is
not very labour intensive in most systems.
- Rainwater
harvesting reduces the accumulation of salt in the soil, which is detrimental
to root growth.
Disadvantages
- Limited rainfall can limit the supply of
rainwater.
- If
not installed properly, it can attract mosquitoes and waterborne diseases.
- Complex
constructions may be costly costs and may require trained professionals.
- Improper construction of tanks may cause leakages and in the
case of metal tanks it may also cause problems like corrosion harming the water
quality.
- The initial cost
of installation is high.
- Regular maintenance is needed, storage capacity limits
Future of Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting systems serve as an alternative decentralized water source, especially at a time when groundwater availability is declining and municipal water infrastructure is facing high replacement costs. The use of decentralized rainwater harvesting systems is growing nationally and internationally, especially in industrialized countries such as Asia, Europe, and the US.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is one of the best ways to solve the world's water scarcity problems. It’s highly useful for large scale applications and brings about a lot of savings in water bills. Rainwater harvesting protects water, money, and the environment.







.png)




No comments yet