Types of impellers in centrifugal pumps and applications
What is
What is an impeller in a centrifugal pump?
An impeller
is a rotating component of centrifugal pump with vanes or blades that
accelerates fluid outwards radially from centre of rotation. Impeller impart
energy to the fluid being pumped. It transfers mechanical energy from pump’s
drive to kinetic energy in fluid.
Most common type of impellers and application.
There are
three basic impeller designs. They are as follows:
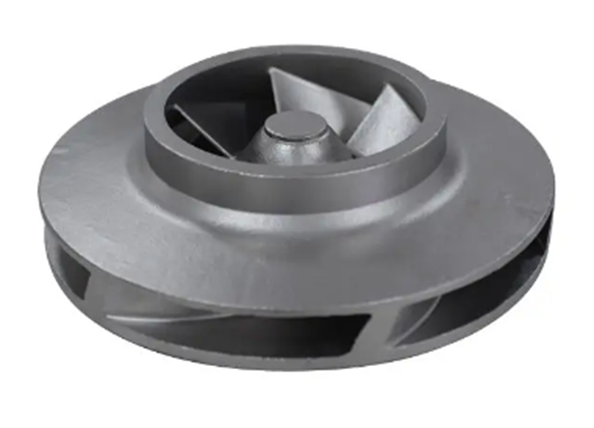
Closed impellers
These types
of impellers have their vanes sandwiched between two solid circular plates. The
liquid travels through the channels between the plates. This design creates the
most efficient flow. The flow enters the impeller through centre and exits
through outer periphery of impeller. This is the most common type of impeller.
Application:
Mainly intended for liquid that are free of solid/suspended particles and less
viscous.

Semi-open Impellers
These
impellers have one side of vanes attached to a circular plate and other side is
exposed to the interior of pump housing. Instead of being sandwiched between
two plates, these impellers have one side open. This design is less efficient
than closed impeller, since the liquid is immediately interacting with rest of
fluid.
Application:
Mainly intended for liquid that has small amounts of solid/suspended particles
and more viscous.
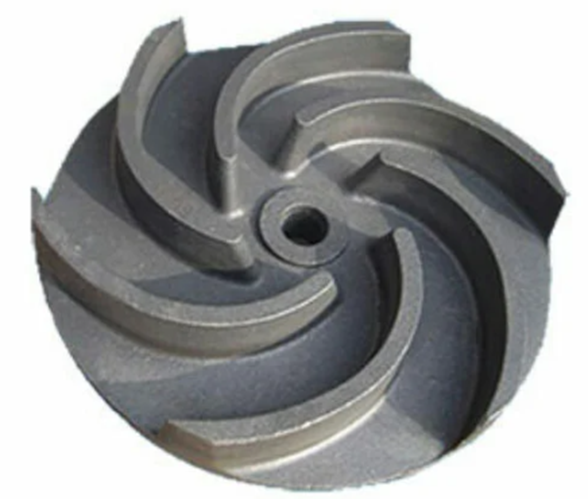

Open impellers
These
impellers have vanes that are open and are not enclosed by any plates. The
efficiency of these impellers are very less than that of the closed impeller.
This is due to the fact that, liquid flowing into pump casing interacts with
liquid that is already in the casing causing decrease in efficiency.
Application:
Pumps with these impellers are able to handle more suspended solids and viscous
liquid.











No comments yet