Water management practices - The fundamentals of Hydroponic system
Water management practices - The fundamentals of Hydroponic system
What is hydroponics
As a new technology in precision farming, hydroponics has gained popularity
throughout the world. Hydroponics refers to the process of growing plants in
nutrient-rich water-based solutions. Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation
system, here the root system is supported using an inert medium such as
perlite, coco coir, clay pallets, peat moss, compost, vermiculite, etc. The
basic principle of hydroponic is to allow the plant’s roots to come in direct
contact with the nutrient solution such as N-P-K mix, Calcium nitrate, Epsom
salt (magnesium sulphate), Ammonium nitrate, Hoagland solution) while also
having access to oxygen, which is essential for proper growth.
Components of the hydroponic system
1.
Growing chamber
Anything other than metal or a material that corrodes or reacts with the
nutrient solution can be used as a growth medium. There are many ideas for
growing a tray, it can be perforated plastic, square, round, or rectangular, so
you just must look around or come up with the simplest design.
2.
Reservoir
The size of the tank depends on several factors, how much space you reserve for
hydroponics, the number and types of plants you grow, and the water needs of
the plant.
3.
Submersible pumps
If you know the minimum amount of water pumped through the system, choosing a
pump is easy. When choosing a pump, it is important to consider how high the
water line of the tank pumps water to the roots.
4.
Delivery tubes
The dosing tubes are simply the medium that sprays the water/nutrient solution
upwards so that the necessary minerals are transported into the grow room to
the plant roots and back to the tank.
5.
Aerators or air pumps
The air pump is specially placed in the tank to help increase the amount of
dissolved oxygen in the water and keep the water saturated with oxygen.
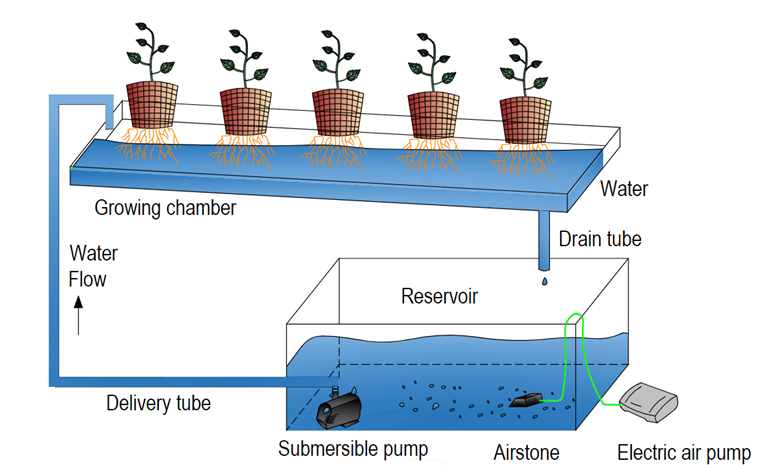
Fig.1: Components of hydroponics system
Types
hydroponics
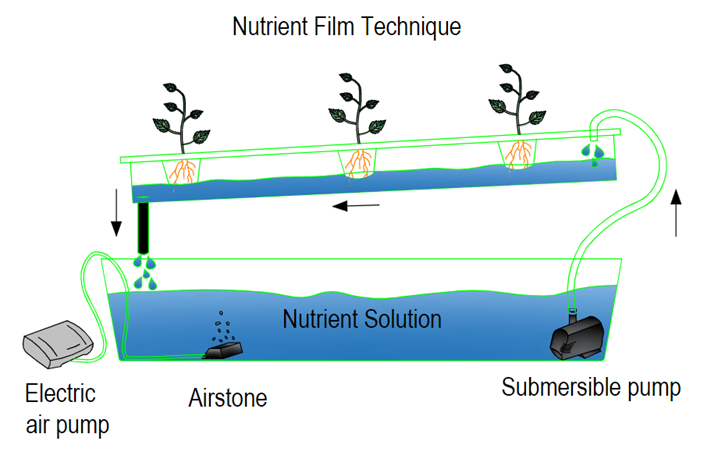
Nutrient film technique
A nutrient film technique is a hydroponic practice in which
all the nutrients that plants need for growth are dissolved in a very shallow
stream of water, which is circulated past their bare roots in a watertight
channel.
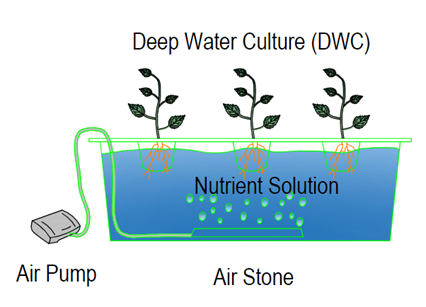
Deep water culture
DWC systems use nutrient solutions suspended in net pots
with a growing medium for securing the roots. Plants are placed in net pots
with the growing medium on top to provide air directly to the roots.
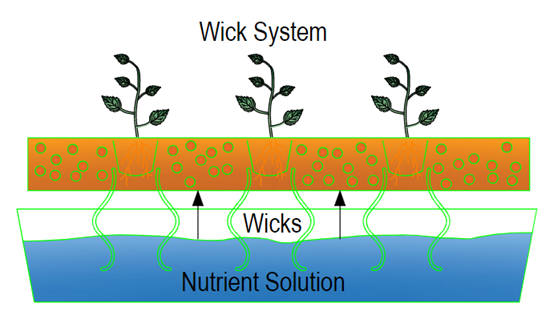
Wick system
The wick system is the simplest type of hydroponic system
that does not require electricity, pumps, or aerators. Among the different
types of hydroponic systems, it is the only one that can be a completely
passive system, which means that no electricity is needed. Since wick
hydroponic systems do not supply the plant with a large amount of nutrient
solution, these systems only work well for houseplants and small herbs. Plants
that do not require a lot of water grow well in wick systems.
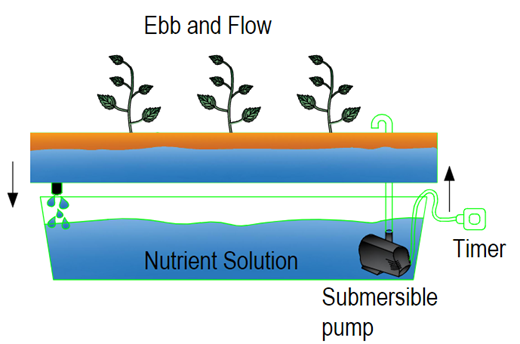
Ebb and Flow
In ebb and flow systems, plants are placed in large grow
beds filled with growing medium. The grow bed is filled with nutrient solution
until it reaches a certain point. Water only gets a few inches below the top of
the growing medium, so it doesn't overflow. A timer controls the power of the
water pump. After running for a predetermined amount of time, the timer turns
the pump off, allowing the water to flow back through the pump and drain the
grow bed completely.
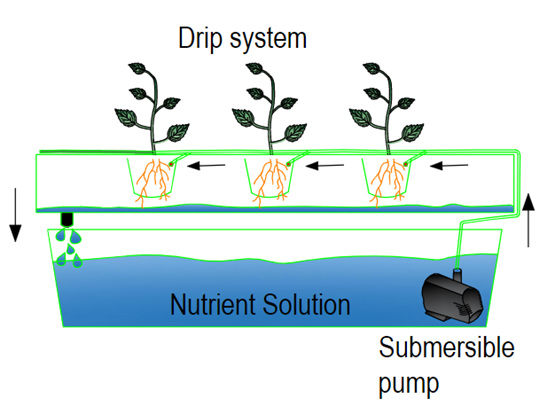
Drip system
Drip hydroponic systems are easy to use, set up and
configure in many different ways, making them ideal for those looking to make
changes. In these systems, the nutrient solution is pumped through pipes
directly to the roots of the plant. The ends of the tubes have drop detectors
that allow the nutrient solution to flow at an adjustable rate that saturates
the growth medium.
Drip hydroponic
systems can be non-circulating or recirculating systems. Non-circulating
systems drip slowly and provide nutrients to the plant at a constant rate.
Recirculation System Excess nutrients flow back into the tank as shown in the
figure below.
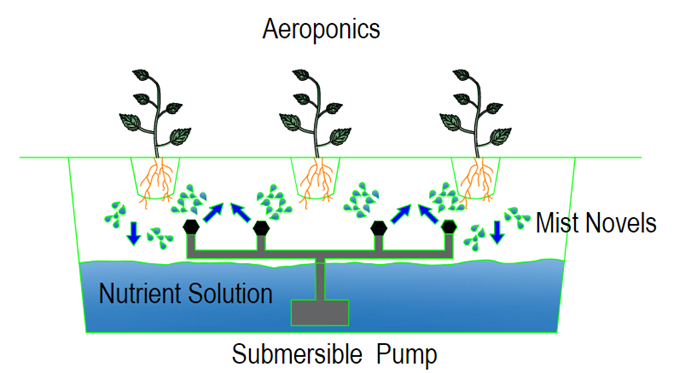
Aeroponics
In an aeroponics system, plants are suspended in the air and
a nutrient solution is sprayed onto the plant's root system. The nutrient
solution is pumped into a pipeline equipped with fog nozzles. As the pressure
increases, the mixture sprays the roots of the plant and the solution falls
back into the tank.
Can organic fertilizers be used in hydroponics?
Organic fertilizers can also be used in hydroponics with
proper precautions because organic fertilizer can attract pathogens and in this
kind of hydroponic system if pathogen infestation takes place, it will be
really very harmful, or it can actually take away the total planting system.
How to know the required quantity of nutrients for the
solution
The drip system is a very common and simple technique that
can be used for providing even solutions to each of the plants individually and
the excess nutrient solution can be either return back to the reservoir or we
may not even prepare that solution if we know the exact amount of nutrient that
is required for the particular plant and that comes with a few experiences
while you actually run this kind of system for some time.






.jpg)
.png)




No comments yet