What Is Water Application Uniformity? Why Is It Important?
A blog describing the importance of uniformity of surface irrigation.
Uniformity of surface Irrigation is a measure of how evenly water is applied on a field. It is commonly referred to as distribution uniformity (DU) and expressed as a percentage. When an irrigation system applies water at a high uniformity, it is possible to achieve a high irrigation efficiency. Similarly, when irrigation is uniform, crop production and quality is often higher and boost revenue potential. Low irrigation uniformity cannot be improved by management of irrigation frequency or duration.
Importance of distribution uniformity
No irrigation system can apply water perfectly uniform across a field, but a DU less than 70% is considered poor for pressurized systems. Ideally, the DU of a pressurized system should be maintained at 85% or higher. Distribution uniformity (DU) is important to achieving efficient irrigation and nitrogen management with pressurized irrigation systems.
The importance of applying water uniformly with pressurized systems is shown in figure.
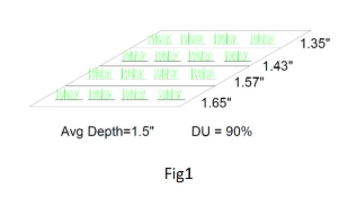
Fig.1 represents an average depth of applied water of 1.5 inches with a distribution uniformity of 90 percent. The average applied water in the ¼ of the field receiving the least water was 1.35 inches and the average applied water in the quarter of the field receiving the most water in the field was 1.65 inches. The difference is only 0.15 inches above and below the target of 1.5 inches.
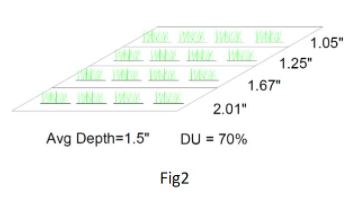
Fig.2 shows a situation where the average depth of applied water is 1.5 inches. However, the applied water ranged from a minimum of 1.05 inches in the ¼ receiving the least water and a maximum of 2.01 inches in the ¼ of the field receiving the most water. This represents nearly a 2 times difference in applied water. If extra water is applied to make sure the low ¼ receives 1.5 inches of water, then the amount of water applied in the high ¼ would be even greater and at more risk of overwatering the crop.
Water application uniformity in irrigation systems
Evaluation of water application uniformity is essential for farming operations that use centre pivot and linear irrigation systems.
Irrigation systems require attention and maintenance, like other farm equipment. It is important to test the uniformity of water distribution and application in a centre pivot mainline irrigation system, just like how farmers inspect their pumps, tractors, generators, etc.
Evaluation of irrigation water application uniformity prevents problems of over or under irrigation on specific areas of the field. Uniform water application ensures even crop growth, nutrient uptake, and fertigation.
Distribution uniformity in centre pivot and linear irrigation system
Center pivot irrigation system rotate around a pivot point, usually located in the centre of a field. Linear move irrigation systems move in a straight line (forward or reverse) and cover square or rectangular field areas.

Sprinklers installed along the main pipeline deliver water to crops as the system moves across the field. The height and spacing of the sprinklers are key to achieving the uniformity of application.
The uniformity of centre pivot or linear move irrigation systems is influenced by nozzle type and size, distribution of water flow, pressure head and wind.
Center pivot irrigation systems are equipped with an end gun type sprinkler mounted on the end of the pivot mainline.
Irrigation application uniformity is defined as the system’s ability to apply the same irrigation depth as it traverses a field. Poor uniformity of water application results in under or over irrigation over sections of crop fields. It can also lead to non-uniform distribution of fertilizer and chemicals where fertigation and chemigation are used.
Water application uniformity
The performance of an Irrigation System is evaluated by conducting a water application uniformity test or catch can test. Three common indices for evaluation are Christiansen’s uniformity coefficient (CUC), Heermann and Hein coefficient of uniformity (CUH), and distribution uniformity (DUlq)
Water application uniformity for linear move systems is assessed through the CUC index, while CUH index is used for centre pivot irrigation systems.
Both Linear move and centre pivot irrigation systems can be evaluated for distribution uniformity of irrigation water using the DUlq index.
Testing consists of measuring the amount of water applied by the irrigation system to determine problems and assess the overall water application uniformity.
Steps to assess the uniformity of water application
1. Set the Irrigation water collectors or cans.
On a centre pivot irrigation system, install the collectors along a straight line perpendicular to the direction the pivot travels. The collectors are spaced according to Standard S436 of the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE). In case of linear move system, install the collectors parallel to the main pipeline. Place collector on holder in such a way that all the collectors are at same level above the ground surface.
2. Check weather conditions.
Windy and hot climate can cause water to drift away or evaporate before reaching the cans. It’s recommended to perform the test during a day with calm wind less than 2.2mph and temperature less than 75 degree F.
3. Run the Irrigation system at Recommended settings
The system should be operated at pressure and flow indicated on sprinkler package.
4. Record the amount of water caught by the collectors
Graduated Cylinders are used to measure the amount of water accumulated in each collector.
5. Plot data to identify the water application problems.
The horizontal axis indicates the distance from the pivot point. The vertical axis is the Depth of water collected. From the graph different problem of water application can be identified.
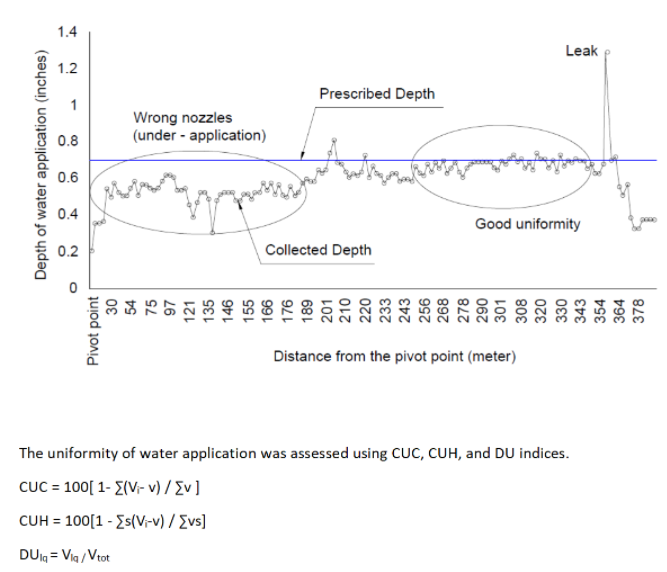
i = number used to identify each collector
Vi = water caught by each collector
V = average volume of water(ml) over all collectors
S = distance of collector from pivot point
DUlq = low quarter Distribution Uniformity
Vtot = average of all water measured from all collectors
Vlq = average of the lowest quartile after sorting the water depth recorded from largest to smallest
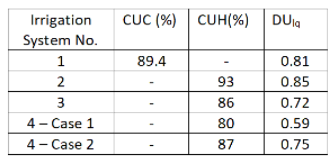
Table shows result of Water Application Uniformity test on four different Irrigation Systems both Linear move and Center pivot.
Value of Coefficient of Uniformity, CUC or CUH above 90% indicate excellent uniformity with no changes required.
Irrigation system 2 shows excellent uniformity. Irrigation System 1 (linear move system) number 3 (centre pivot system) have a coefficient of uniformity of 84.9 and 86 respectively which show good uniformity (85 and 90 percent) with no major changes unless any problem is identified.
The System No 4 is a pivot Irrigation system with a fair coefficient of uniformity 80 to 85 percent. The coefficient of uniformity is increased to 87 percent by replacing some nozzles.
The Distribution Uniformity DUlq index indicates how evenly water is distributed over an area. A DUlq of 85 percent or greater indicated excellent distribution of water. A DUlq equal or less than 0.7 indicates that system maintenance is required.
Water application uniformity tests help you ensure your irrigation system is working for you.
The water application uniformity test allows farmers to analyse if the irrigation systems is performing properly. Preventing malfunctions of irrigation systems could reduce under or overapplication of water and chemicals.






.png)




No comments yet